Lead Toxicity
Symptoms
Musculoskeletal system, arthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid, gout, low back pains, rickets
Nervous system
abnormal brain function, blindness, convulsions, deafness, dyslexia, encephalitis, encephalopathy, epilepsy, fatigue, insomnia, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, vertigo
Cardiovascular system
arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis
Digestive system
abdominal pain, colic, constipation, indigestion, liver dysfunction, weight loss
Vascular system
anemia
Reproductive system
spontaneous abortions, impotency, infertility, diminish libido, menstrual difficulties, sterility, stillbirths
Glandular system
adrenal insufficiency, hypopituitarism, hypothyroidism
Excretory system
nephritis, renal dysfunction
Dental
pyorrhea, tooth decay
Psychological
anxiety, poor concentration, mental depression, hallucinations, hyperkinesia, memory impairment, mental retardation, mood swings, nightmares, psychotic behavior, schizophrenia
Effects of Lead
- Blood– inhibits enzymes associated with hemoglobin synthesis, and increases the rate of destruction of red blood cells. End result is fatigue.
- Bones – lead is incorporated into bone in preference to calcium.
- Brain – can inhibit copper-dependent enzymes needed for neurotransmitters (dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine). End result is hyperactivity.
- Energy – inhibits copper and iron-dependent enzymes in the Krebs cycle required for energy production. End result is fatigue.
- Kidneys – lead can raise uric acid levels and impair kidney function. End result is gout.
- Minerals – lead displaces and can cause deficiency or bio-unavailability of calcium, zinc, manganese, copper and iron.
- Thyroid gland – lead interferes with iodine uptake by the thyroid, and can inactivate thyroxin, the hormone.
Sources of Lead Toxicity
drinking water, that is soft and acidic and erodes lead from lead piping, food from lead-lined containers, lead based paint, cosmetics, cigarettes (because of the lead-containing insecticide applied to tobacco), the burning of coal, peeling lead-based paint or plaster and lead-based paint coated pencils often chewed on by children and motor vehicle exhausts. Children can also be born with elevated lead, passed through the placenta from their mothers. Diets deficient in calcium, magnesium, or iron increase lead absorption.
Detection of Lead Toxicity
Blood lead testing is not accurate in detecting chronic lead toxicity. Within 30 days of exposure, most lead is removed from the blood and stored in body tissues. Blood challenge tests can detect a certain amount of lead poisoning. Hair testing has been shown by the Environmental Protection Agency to be a good method of testing for lead poisoning. Several hair tests may be necessary before elevated lead levels are revealed.
Nutritional Support
Vitamin C, sulfur and calcium are used in lead detoxification. They may be effective; however, the major components appear to be B-15 (pangamic acid) and B-17 (laetrile). It may also be helpful to use apple pectin as a binding agent in the digestive tract.
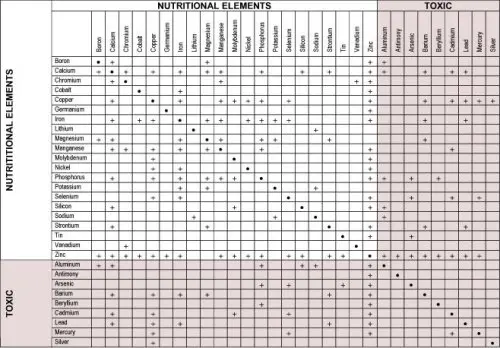
Interaction Chart
![[ZHZP] Zeolite Pure](/web/image/product.template/3512/image_1920/%5BZHZP%5D%20Zeolite%20Pure?unique=ae82545)
![[ZHZV] Zeolite-AV](/web/image/product.template/3513/image_1920/%5BZHZV%5D%20Zeolite-AV?unique=07da5f8)